In moments of crisis, every second counts. When faced with a medical emergency, the swift arrival of an ambulance can often mean the difference between
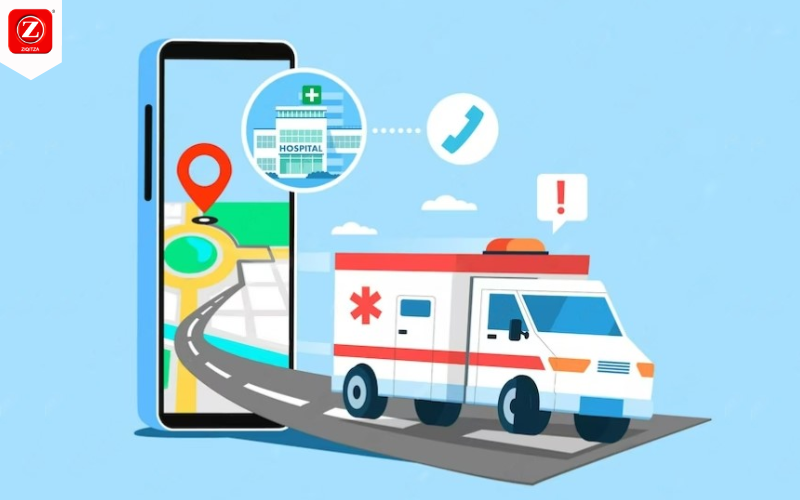



In moments of crisis, every second counts. When faced with a medical emergency, the swift arrival of an ambulance can often mean the difference between
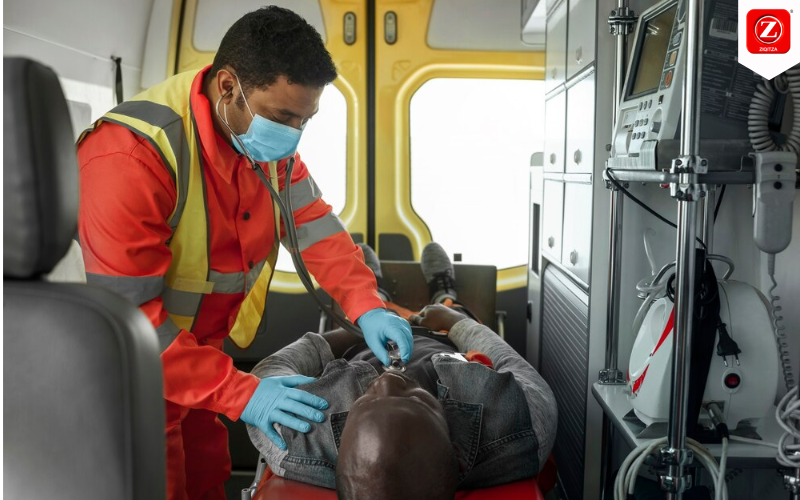
In this critical field of emergency medical services (EMS), Ziqitza Health Care Limited leads from the front, providing top-notch ambulance services across various regions. However,
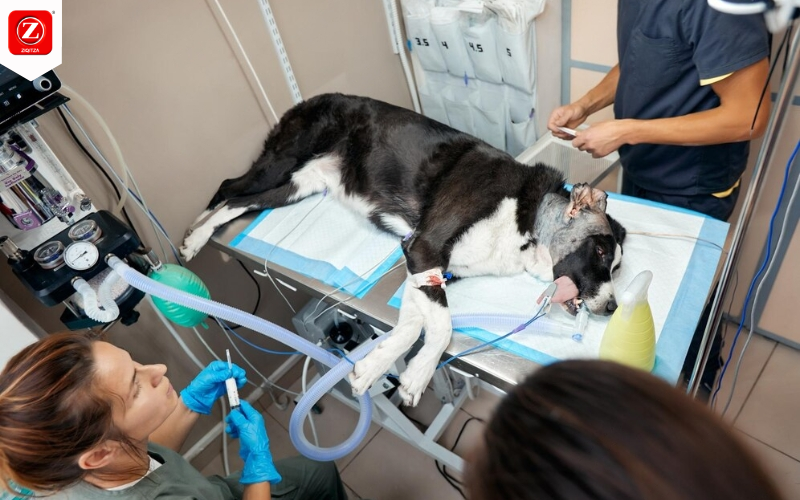
In recent years, the demand for pet healthcare services has skyrocketed, reflecting the growing recognition of pets as integral members of our families. Like humans,
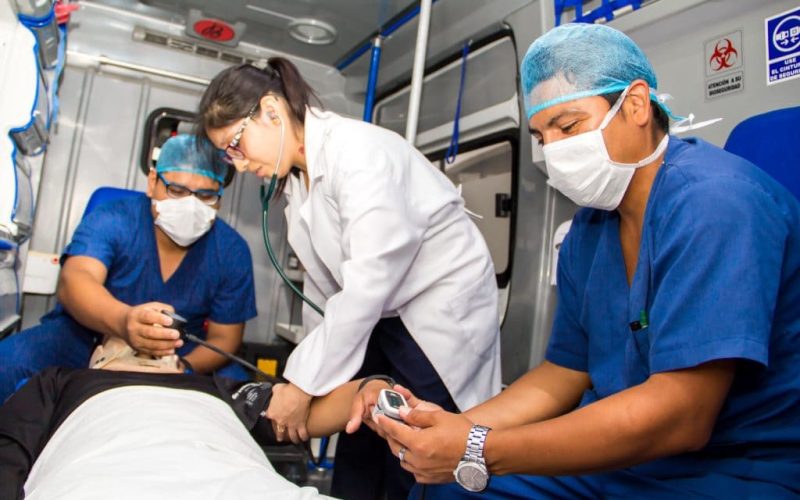

Climate change isn’t just about rising temperatures or extreme weather events; its effects extend far and wide, affecting various sectors of society. One critical area
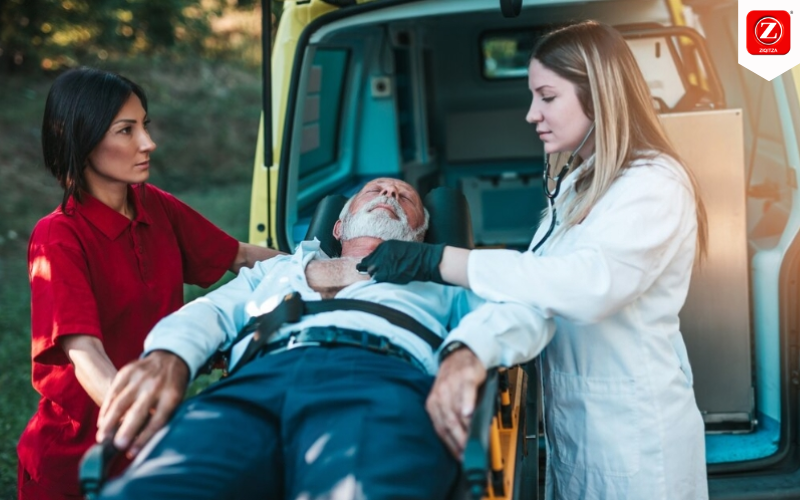
As our population ages, the demand for specialized healthcare services for senior citizens continues to rise. Among these essential services, emergency medical assistance stands out

In the hustle and bustle of urban life, emergencies can strike at any moment, demanding swift and efficient medical response. Navigating through congested streets, battling

In the vast and diverse landscape of India, ensuring timely and efficient emergency healthcare services poses a significant challenge. To address this, the partnerships between

Urban healthcare and ambulance services in India face a large number of challenges, with rapid urbanization increasing the complexities of emergency response. In this realm,

India with its diverse climatic conditions is no stranger to the challenges posed by extreme weather conditions. From scorching heat waves to devastating floods and
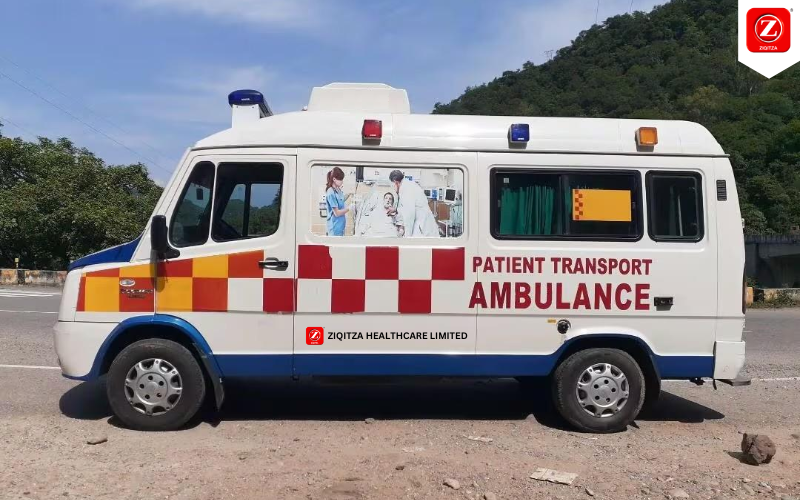

In the face of natural disasters and emergencies, a well-coordinated and efficient response is paramount to saving lives and minimizing damage. One organization that has
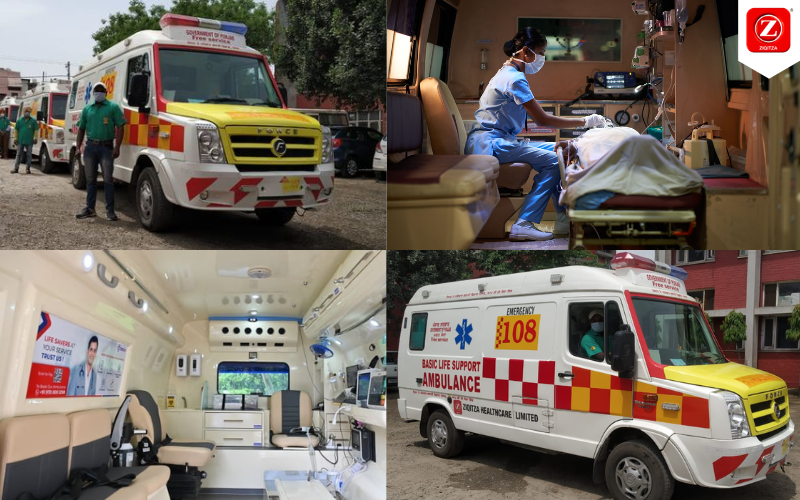

In the rapidly changing landscape of healthcare, the intersection of technology and patient care has witnessed remarkable advancements, particularly in the field of ambulance services.
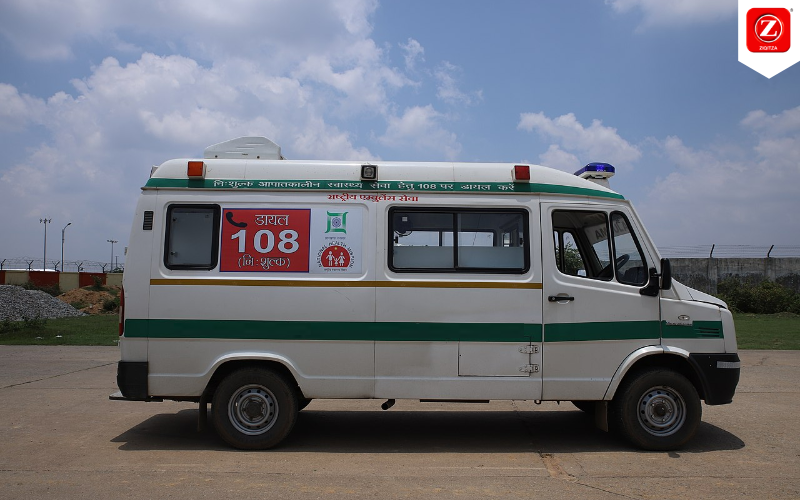

In the landscape of rural areas, access to emergency healthcare services has been a longstanding challenge. The limited availability of healthcare facilities, coupled with the
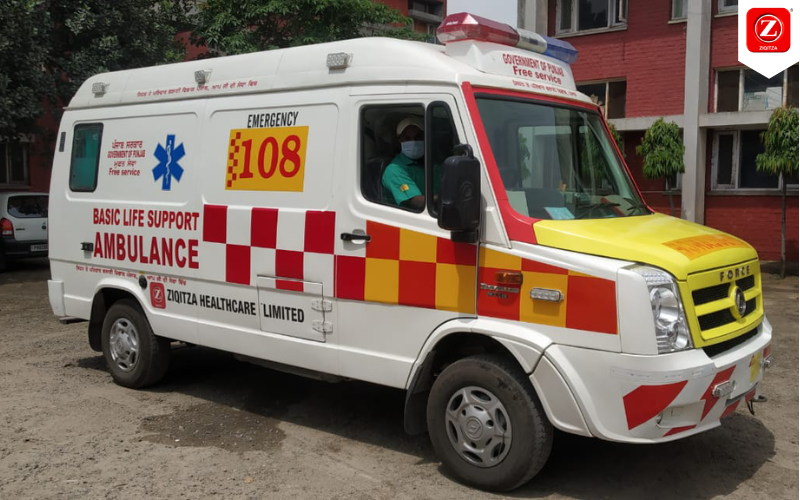

In the ever-changing landscape of emergency medical services (EMS), innovation is the key to saving lives and improving patient outcomes. One organization at the forefront

In a country as vast and diverse as India, the need for efficient emergency healthcare services is paramount. Recognizing this, Ziqitza Healthcare ltd has emerged
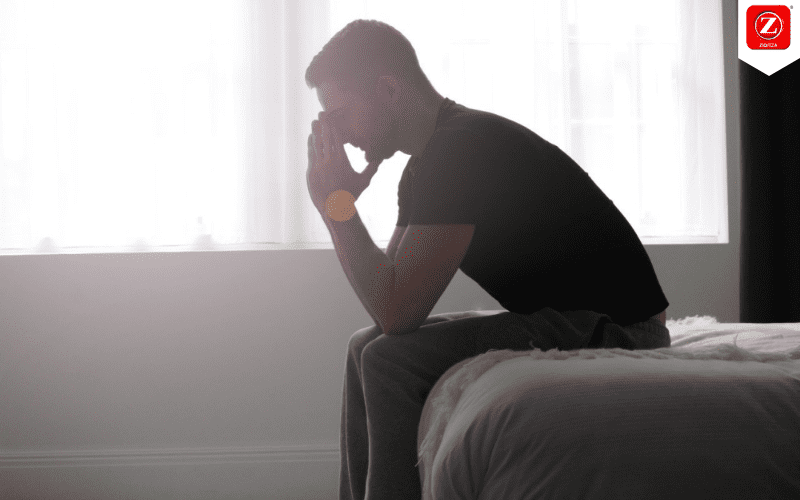

A person’s mental health is just as important as their physical health in a society where physical health is frequently given priority. Sadly, there is

Time is of the essence and every second counts in the field of emergency medical services. Ziqitza limited, a distinguished emergency ambulance service provider, is

In the rapidly changing landscape of healthcare, Emergency Medical Services (EMS) play a critical role in saving lives and providing timely medical assistance. As we

In the fast-paced world of emergency medical services (EMS), the mental health of personnel is often overlooked. As the backbone of emergency response, individuals working

In this dynamic realm of healthcare, the need for innovation extends beyond medical advancements into domains that impact our environment and financial resources. Ziqitza Healthcare,
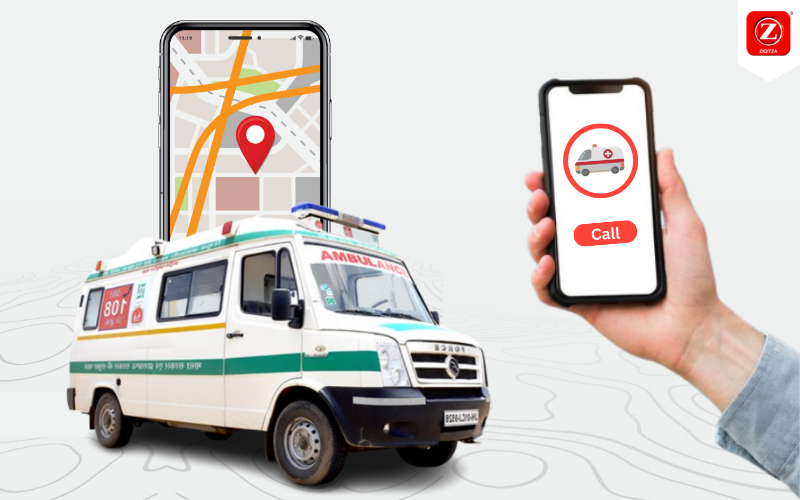

In today’s digital age of healthcare, the integration of telemedicine and ambulance services is proving to be a transformative synergy, promising a future where medical